Our Environment
OUR ENVIRONMENT
Basic Terms
Basic Terms
Environment: Anything which surrounds an organism is said to form its environment. The surrounding can be changed by the animal or plant itself. In simple words, environment is the sum total of all external conditions and influences that affect the life and development of an organism.
Ecology: It is the study of relationship between the organisms and the
environment.
Habitat: It is the natural living condition of an organism or animal.
Biodegradable substances: These are those substances which are
broken down into simpler, harmless substances in nature within due course of
time by the biological process such as action of micro-organisms like certain
bacteria.
Example: paper, wood, cloth etc.
Non-biodegradable substances: These are those substances which cannot be broken down into
simpler, harmless substances in nature.
Example: DDT, plastics, polythene bags etc.
Biosphere: All ecosystems taken together make up the biosphere. Biosphere
is the zone, including the earth’s surface, the adjacent atmosphere, and the
underlying crust where life can exist.
Ecosystem: An ecosystem may be defined as a
structural and functional unit of the biosphere in which living and non-living
component interact together to form stable and self supporting system. The term Ecosystem was coined by
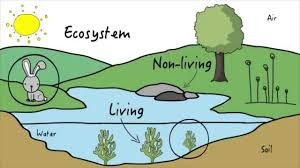 |
| Ecosystem (Biotic & Abiotic Component) |
Components of ecosystem: There are two components of ecosystem.
Biotic component: Biotic component consists of living part
of the environment such as plants, animals, human beings, micro-organisms etc.
Abiotic component:
Abiotic component consists of non-living part of the environment such as air,
water, soil etc.
Types of Ecosystem: There are two types of ecosystem.
Natural Ecosystems: These ecosystems operate in the nature
by themselves without any human interference.
Artificial
ecosystems: These are maintained by man and hence are
also termed man-made or made-engineered ecosystems.
 |
| Artificially Maintained |
Example:
Croplands, orchards, gardens, parks etc.
Producers:
These
are those organisms which can make their own food. This includes all green
plants and certain blue-green algae. These organisms can utilise solar energy
with the help of photosynthetic pigments to form glucose. Producers ultimately
produce the food for all other members of the community.
Consumers:
All animals are consumers. They cannot make their own food.
Therefore, they utilize materials and energy stored by the producers.
Example:
i. Primary
consumers or Herbivores.
i ii. Secondary consumers or Carnivores.
ii iii. Tertiary
consumers or omnivores.
Decomposers: These
are those organisms which feed on dead decaying matter. These include bacteria
and fungi.
Functions of decomposers:
1. Decomposers
cleanse the earth of organic remains and can therefore, are termed as natural
scavengers.
2. Decomposers
create space for newer generations of organisms.
3. Decomposers
release minerals and other raw materials trapped in organic matter.
Food
Chain:
Food chain is a sequential interlinking of
organisms based on their feeding habit. In simple words, a list of living
organisms showing “who eats whom” is called a food chain.
i.e.,
Example:
 |
| Food Chain |
 |
| Food Chain |
 |
| Food Chain |
Properties of food chain:
1. Usually,
there are four or five tropic levels in a food chain.
2. A food chain is always straight and
proceeds in a progressive straight line.
3. In a food chain, there is unidirectional
flow of energy.
4. Shorter food chains provide more available
energy, while longer ones provide little available energy.
5. Only 10% of the energy available at each
tropic level is transferred to the higher level.
Food
Web:
Food web is a network of food chains which
are interconnected at various tropic levels so as to form a number of feeding
connections.
 |
Difference between Food chain and Fod web |
 |
| Food web |
Properties
of food web:
1. Unlike food chains, food webs are never
straight.
2. A food web provides alternative pathways of
food availability.
3. Greater alternatives available in a food
web make the ecosystem more stable.
4. Food webs also help in checking the
overpopulations.
5. Food webs also help in ecosystem
development.
Flow of
energy in an ecosystem:
1. The ultimate source of entire energy, used
by living organisms, is the sun.
2. Of the total solar radiations falling on
the earth, only about 1% are captured by green plants in a terrestrial
ecosystem and converted into food energy by photosynthesis. This energy is
stored as chemical energy of food and finally used by the consumers.
10% Law:
It
was put forth by Lindeman (1942). It is also termed as second law of
thermodynamics or law of entropy. According to this law, on an average, only
about 10% of energy is actually available to the next tropic level.
Biological
Magnification:
The
phenomenon that involves progressive increase in concentration of harmful
non-biodegradable chemicals at different tropic levels in a food chain is
called biomagnifications.
In simple words, some harmful
non-biodegradable chemicals such as mercury, Cadmium etc. enter the bodies of
organisms through the food chains and go on concentrating at each tropic level.
This phenomenon is called bio-magnification or biological magnification.
Ozone
and its Importance:
Ozone (O3) is a form of oxygen.
It is formed by three atoms of oxygen.
In the stratosphere, ozone is being photo
dissociated and generated by the absorption of harmful, ultraviolet (UV) radiations
coming from sun.
Ozone layer is very important for the
existence of life on earth because it absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet
radiations coming from the sun and prevents them from reaching the sun.
 |
| Ozone Depletion |
 |
| Ozone layer and its Depletion |
Ozone
depletion and its cause:
The
thinning of ozone layer is commonly called ozone depletion. Ozone is being
depleted by air pollutants like CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), methane (CH4)
and oxides of nitrogen (NO). The excessive use of the fossil fuels and other air pollutants is also one of the major cause of the ozone depletion. The hole in the ozone layer called as ozone hole
was first discovered over Antarctica in 1985.
Harmful
Effects of Ozone depletion:
The
ozone depletion has following harmful effects.
1. Ultraviolet
radiations cause skin cancer.
2. These
cause damage to eyes and also can cause increased incidence of cataract disease
in eyes.
3. These
cause damage to immune system.
4. Ozone
depletion also causes global rainfall and ecological disturbances.
Wastes
and moles of waste disposal:
“Waste
disposal” literally means “getting rid of waste”.
Some prominent methods of waste disposal
are:
1. Landfills: In
urban areas, majority of the solid wastes are buried in low lying areas to
level the uneven surface of land. This method of waste disposal is commonly
called landfills.
2. Recycling of Wastes: Number
of solid wastes (paper, plastics, metals, etc) can be recycled by sending them
to respective recycling units.
3. Preparation of Compost:
Household waste such as peeling of fruits and vegetables can be converted into
compost and used as manure.
4. Incineration: Incineration
is the process of burning of substances at high temperature and ultimately
converting them into ashes. It is carried out in an incinerator.
5. Production of biogas and manure:
Biodegradable wastes can also be used in biogas plants to generate biogas and
manure.
................................
the remaining content is under process
the remaining content is under process
With Regards
Riya Gupta
Also See:
Labels: Biology, Science (10th)








3 Comments:
Really nyc 1
thaku g
Thankyou sir for providing such helpful study material
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home